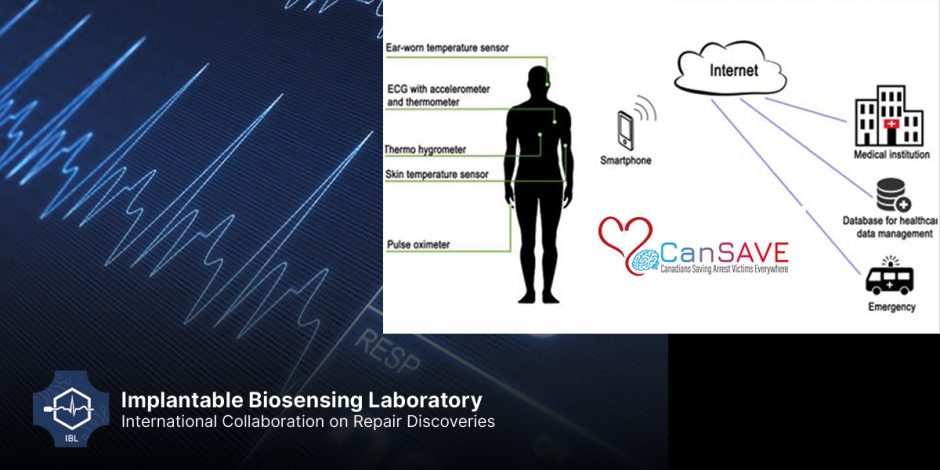
Effective and accurate multimodal sensors that can recognize loss of cardiac pulsation and circulation and then automatically notify a dispatch center of the location of the sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) patient will ensure that each SCA is “witnessed” immediately at the time of collapse. Such sensors could increase the chance of survival in the current treated but “unwitnessed” group from 4%-16%. Sensors will also double the number of patients treatable by paramedics (rather than declaring futility due to lengthy intervals between collapse and discovery). Widespread use of biosensors would increase the number of cardiac arrest survivors nationally from 1,800 to 6,000 per year. We are collaborating with CanSave to design and develop SCA sensors
More Information:
Visit: https://cansave.ubc.ca/work-us
Supported By:
